Your Partner in Optimum Health!
 menu
menu- Servicesexpand_more
- Patient Processexpand_more
- Aboutexpand_more
- Events
- Blog
- Patient Portal
- Contact Us
- Shop
Your Partner in Optimum Health!
August 01, 2020
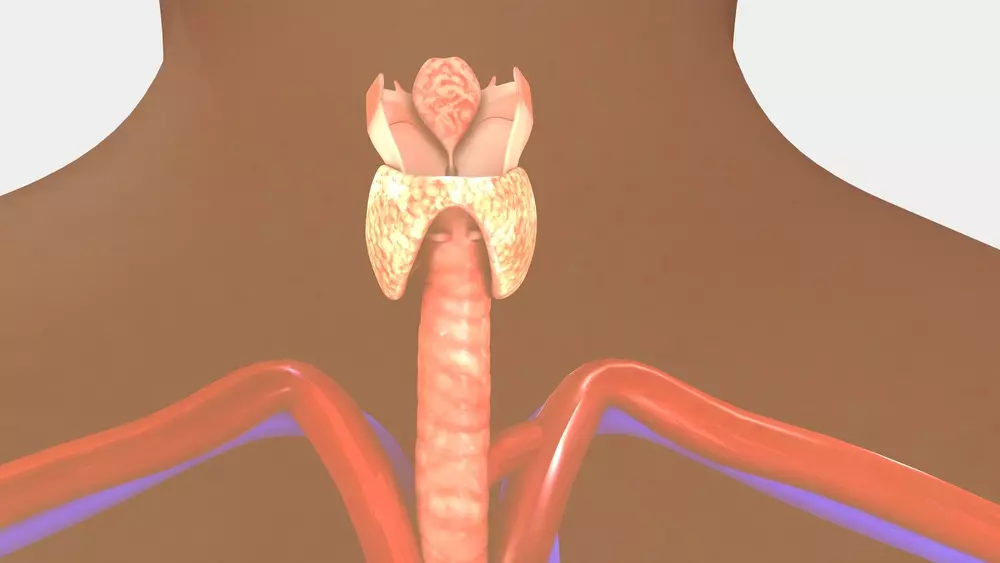
Although your thyroid is a relatively small gland in your neck, it has a powerful influence on your weight, appearance, moods, and general health. When your thyroid stops producing the correct amount of hormones, you can experience anxiety, hair loss, weight changes, and many other negative symptoms. Fortunately, you can begin the process of fixing this issue by getting thyroid testing at the Medical Transformation Center in Louisville, KY.
Since thyroid diseases can lead to very negative health consequences, it’s important to diagnose and treat your thyroid issues at an early stage. Many thyroid diseases develop when your thyroid produces inadequate or excessive amounts of hormones. Hypothyroidism occurs when your thyroid does not make enough hormones. In contrast, hyperthyroidism develops when this gland produces too many hormones.
We can perform diagnostic tests to analyze the functionality of this gland and determine whether you have hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, or another thyroid disorder. You should get thyroid testing when you are experiencing unexplained weight changes, emotional problems, or other warning signs of thyroid disorders.
Since your thyroid influences your metabolism, an unexplained change in your weight can be a sign that this gland is not functioning properly. When you have hypothyroidism, your metabolism will slow down, and you may gain weight quickly.
In contrast, if your thyroid is producing too many hormones, your metabolism will increase and you will quickly lose weight. Although this change might please you, you should not ignore your weight loss. Losing weight without changing your activity level or diet can be a sign that you have an illness or other condition, and you should receive medical testing to determine the cause of this change.
The behavior of your thyroid also affects your moods. When your thyroid is too active, you might experience anxiety, anger, and frustration. For instance, you might get very nervous about minor problems or get into frequent fights with your coworkers, friends, and family members. These unexplained emotional changes can be very upsetting, and your anxiety and anger can cause conflict in your professional and personal relationships.
When your thyroid stops functioning properly, you might develop a number of digestive challenges. If your thyroid is too active, you might notice that you have loose stools after you eat. If your thyroid does not produce enough hormones, you may become constipated.
Some thyroid issues will cause you to develop nodules and lumps on your neck. These irregularities may appear when your thyroid has become swollen. A lump may be a sign that you have thyroid cancer or another medical issue. If you notice any of these issues, you should not ignore these problems. Instead, you should schedule an appointment so that we can use thyroid testing to determine the cause of these changes.
Changes in the functionality of your thyroid can affect your response to hot and cold temperatures. If you are suffering from hypothyroidism, you might become very sensitive to cold temperatures. For example, you may shiver in relatively warm temperatures and frequently wear sweaters and jackets to stay warm. In addition, your feet and hands can become very cold.
If you have hyperthyroidism, you may also develop a sensitivity to hot temperatures. You might begin to sweat excessively and suffer from hot flashes.
It’s normal to lose multiple strands of hair every day. However, if you are losing large amounts of hair each day or noticing thin patches on your scalp, you might be experiencing hormonal changes that are damaging your hair. In particular, hyperthyroidism can cause you to experience noticeable hair loss.
Several different thyroid disorders can cause you to develop acne and other skin issues. Hypothyroidism may cause your skin to become very dry. If you have an overactive thyroid, you might develop oily, moist skin.
An improperly functioning thyroid gland can damage your eyes. You might develop red, dry, or watery eyes. Further, you could have issues with double vision, struggle to close your eyelids, or have other vision changes. Your eyes might also begin to bulge. Since this symptom develops slowly, your friends, family members, and coworkers may notice this issue before you do.
If you find yourself struggling to stay focused and finish tasks in an accurate, careful manner, you might be suffering from hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Both of these thyroid disorders can cause you to become easily confused or forgetful. You might frequently lose your keys and important objects, forget the names of people you recently met, or have difficulty staying focused when you are working on a complicated task.
Your thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in your neck that produces a variety of important hormones. These hormones affect how your body uses the energy in your food. Your thyroid accomplishes this task by making thyroxine and triiodothyronine, also known as T4 and T3. When your thyroid is working properly, your body will have sufficient amounts of these hormones.
If you develop hyperthyroidism, your thyroid will make excessive amounts of hormones. These unnecessary hormones will speed up your metabolism and cause you to process the energy in your food at a very fast rate. This change can cause you to feel anxiety, develop heart problems, lose weight, and experience other issues.
Sometimes your thyroid produces insufficient amounts of hormones. As your hormones decrease, your metabolism will slow down, and you might feel sluggish and gain weight.
People of all ages and genders can develop hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, and other thyroid problems. In fact, about twenty million people who live in the United States have thyroid issues. That said, certain personal and family traits will impact a person’s chances of developing a thyroid issue during his or her life.
There are a number of conditions and illnesses that will increase your chances of experiencing thyroid issues. For instance, type I diabetes will enhance your risk, and you should consider getting regular thyroid testing if you suffer from this condition. Similarly, type 2 diabetes increases the chances that you will get a thyroid disorder as you age.
In addition to diabetes, having lupus, pernicious anemia, rheumatoid arthritis, and other illnesses will increase your chances of suffering from thyroid issues.
As you might expect, you have a higher chance of developing issues with your thyroid if your parents, siblings, or other relatives have suffered from thyroid problems.
Women are much more likely than men to develop thyroid disorders. Further, thyroid issues are more likely to affect people who are age sixty and older.
Going through pregnancy and giving birth to a child can sometimes result in a disease known as postpartum thyroiditis. During this illness, your thyroid will develop issues during the twelve months after you give birth. Early symptoms of this illness can be very similar to the problems caused by hyperthyroidism. For example, you might experience anxiety, lose weight, and develop sensitivity to heat.
Since these symptoms can also resemble the problems caused by postpartum mood disorders, this thyroid issue can be easy to misdiagnose. However, since postpartum thyroiditis can cause you to develop lasting thyroid problems, you should not ignore your symptoms. Coming in for a test will help us determine the cause of your symptoms and begin improving your mood and quality of life.
Physical examinations, blood tests, and other methods can be used to diagnose thyroid disorders.
Performing a physical examination of your body can help us determine more about the condition of your thyroid. During your examination, we will gently feel your neck and look for any growths or other irregularities on your thyroid.
Performing a blood test is one of the best ways to determine whether you are suffering from a thyroid disorder. During this type of test, we will gently draw blood from your arm. Once we have collected your blood, we will use it to analyze the number of hormones, antibodies, or other substances in your body.
In addition to testing your blood, we may use imaging tests to check for thyroid disorders. For example, we can use an ultrasound test to create images of your thyroid. During this non-invasive test, we will put a cool gel onto your skin. Next, we will put a probe onto your neck and carefully move it over your thyroid. This process will allow us to learn more about the health and functionality of this gland.
You shouldn’t let fear or anxiety about the diagnostic process stop you from getting these important tests. These tests are very straightforward and comfortable. For instance, if you’ve received blood work in the past, you already know that getting a blood draw is a routine medical process that only takes a couple of minutes to perform. Further, you’ll be able to return to your typical activities as soon as we have finished collecting your blood.
Similarly, you shouldn’t feel worried about getting a physical examination of your throat. We will slowly and gently examine this area of your body, and you’ll have a chance to ask us questions as we complete this part of your appointment.
There are a variety of medications, procedures, and other medical treatments that can improve your thyroid disorder. The treatments that work for you will depend on the type of thyroid disorder that we are treating, the severity of this disorder, and other factors.
If your thyroid is overactive, we may prescribe medications that will prevent this gland from producing too many hormones or decrease the severity of your symptoms. Alternatively, you could receive a radiation treatment that will damage the cells in your thyroid and stop this gland from creating unnecessary hormones.
Hyperthyroidism can also be treated by removing your thyroid from your body. After this procedure is complete, you will need to take medication to replace the hormones that your thyroid used to create.
If your thyroid is not producing enough hormones, you can address this problem by taking synthetic hormones. For instance, we may instruct you to take a medication called levothyroxine.
Unexplained fluctuations in your weight, sensitivity to temperature changes, hair loss, and other symptoms may indicate that you are suffering from hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or another thyroid disorder. Instead of living with these unpleasant symptoms, you should determine the cause of these issues with thyroid testing. To learn more about these important tests, contact us today at the Medical Transformation Center in Louisville, KY.