You may have heard the buzz about glutathione in health and wellness circles, but what exactly is it, and why is everyone talking about it? This guide will explore everything you need to know about glutathione, its role in your body, who should avoid it, and how you can incorporate it into your life.
What is Glutathione?
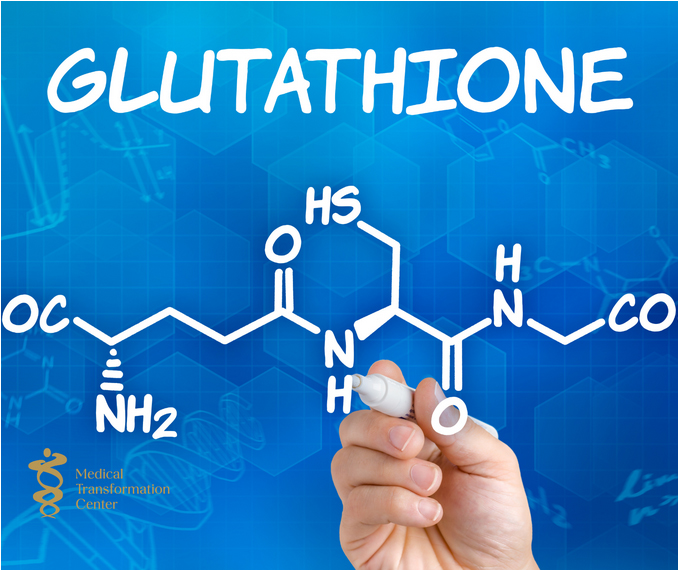
Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant found naturally in your body. Made up of three amino acids (glutamine, glycine, and cysteine), it helps protect your cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. Often called the “master antioxidant,” glutathione is produced by the liver and plays a vital role in maintaining overall health.
What Does Glutathione Do for Your Body?
Glutathione wears many hats when it comes to your health. Its main roles include:
- Fighting Oxidative Stress: Glutathione neutralizes free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and lead to chronic diseases like cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
- Detoxification: It assists the liver in removing toxins and harmful substances from the body.
- Boosting Immune Function: Glutathione helps enhance the immune system by supporting white blood cells, making IV therapy with glutathione a powerful antioxidant essential for pre-surgery patients.
- Skin Health: It is popular for its skin-brightening properties and may help reduce hyperpigmentation.
- Supporting Cellular Repair: Glutathione is essential for DNA repair and maintaining cellular function.
- Joint Heath: Glutathione, a powerful antioxidant, is gaining attention for its potential to support joint therapy, especially in managing conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, as well as potentially safeguarding cartilage, it has become a compelling focus of ongoing research in joint health.
Who Should Not Take Glutathione?
While glutathione is generally safe for most people, certain individuals should avoid supplementation without consulting a healthcare professional. These groups include:
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: The effects of glutathione on pregnancy and breastfeeding are not well-researched.
- People with Low Zinc Levels: Taking glutathione may further deplete zinc, leading to deficiencies.
- Individuals with Allergies to Glutathione Ingredients: Some supplements may contain additives or fillers that can trigger allergies.
Always consult your doctor before starting any new supplement, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking medications.
What Foods Are Good Sources of Glutathione?
Your body can produce glutathione naturally, but you can also boost its levels through your diet. Foods rich in glutathione or its building blocks include:
- Fruits and Vegetables:
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- Avocados
- Tomatoes
- Oranges
- Protein-Rich Foods:
- Whey protein
- Eggs
- Fish
- Cruciferous Vegetables:
- Brussel sprouts
- Cauliflower
- Kale
- Sulfur-Rich Foods (important for glutathione production):
- Garlic
- Onions
Eating a balanced diet with these foods can support your body’s natural production of glutathione.
Can You Have Too Much Glutathione?
Yes, it is possible to have too much glutathione, especially if you’re taking supplements. High doses over a long period may have unintended effects. Over-supplementation can lead to:
- Digestive issues such as bloating or diarrhea.
- Altered zinc levels in the body.
- An imbalance in natural antioxidant levels, potentially causing the opposite of its intended benefits.
The key is moderation. Stick to recommended dosages and consult a healthcare provider to ensure you’re taking the right amount.
What Are the Side Effects of Glutathione?
While glutathione is generally safe, some people may experience minor side effects, especially if taken in high doses or for extended periods. These include:
- Digestive Issues: Nausea, cramping, or diarrhea.
- Allergic Reactions: Mild rash or itching.
- Respiratory Issues (in rare cases): Wheezing or difficulty breathing.
If you notice any severe side effects, discontinue use immediately and seek medical advice.
Wrapping It Up
Glutathione plays a crucial role in maintaining health by neutralizing free radicals, detoxifying the body, and supporting cellular function. While it offers numerous benefits, like all supplements, it should be used responsibly. Focus on eating a diet rich in glutathione-boosting foods, and consult your doctor before adding supplements to your routine.
Understanding how to harness the power of glutathione can be an exciting step toward better health. Stay balanced, stay informed, and give your body the care it deserves!